CPM Precision uses powder bed fusion for additive manufacturing. In this process, a component is melted layer by layer from the starting powder using laser technology.
The component is gradually built up by applying wafer-thin layers of titanium powder to a base plate.
This extremely precise, innovative method is suitable for both prototypes and series production.
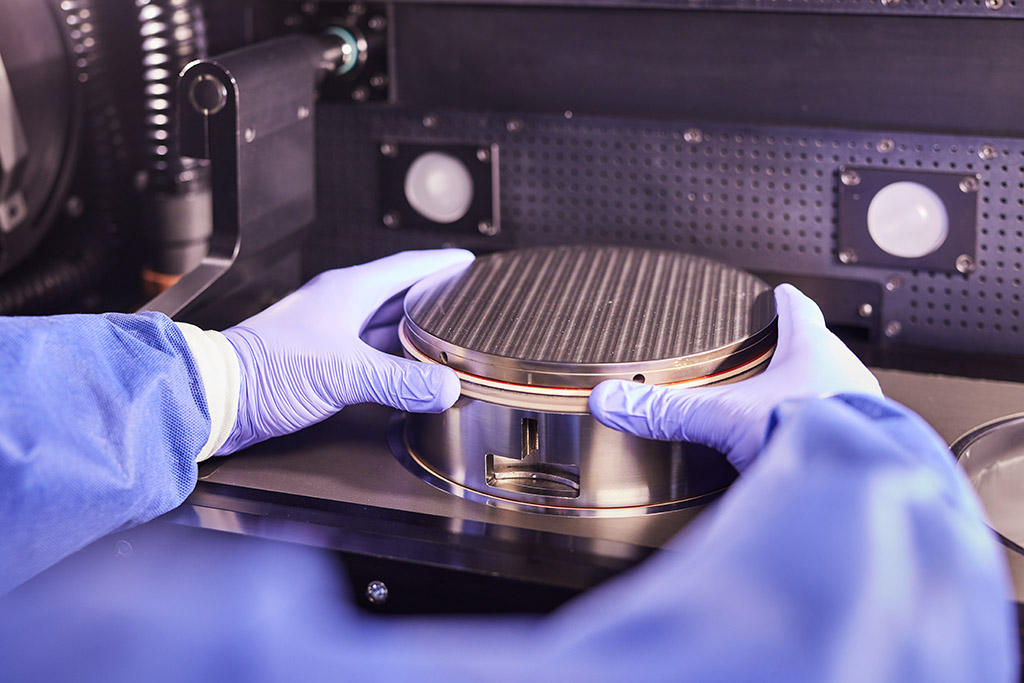
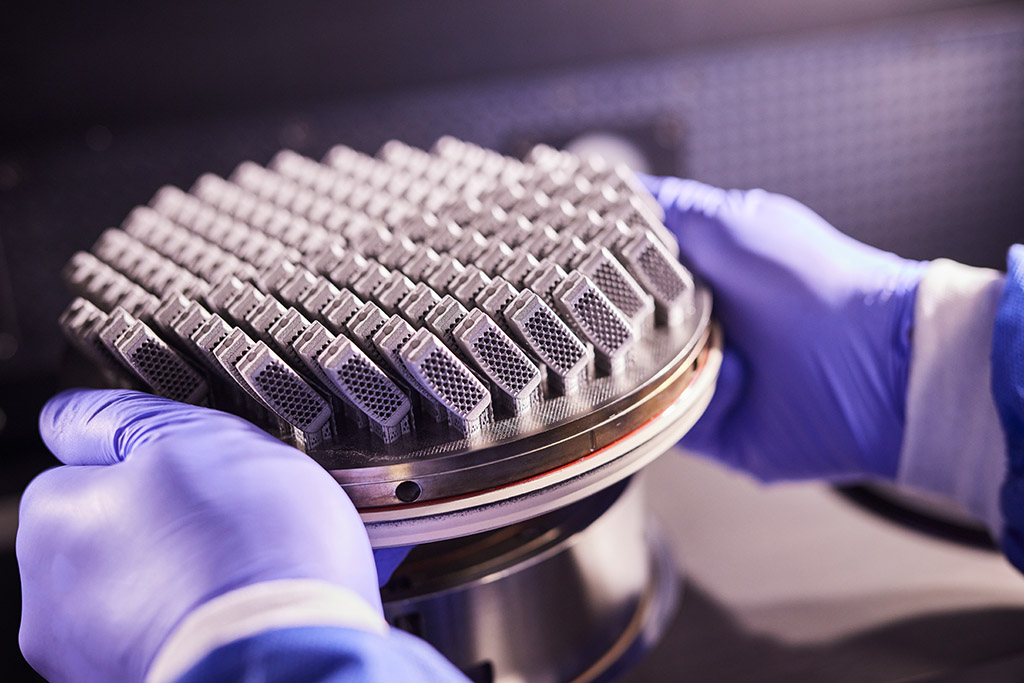
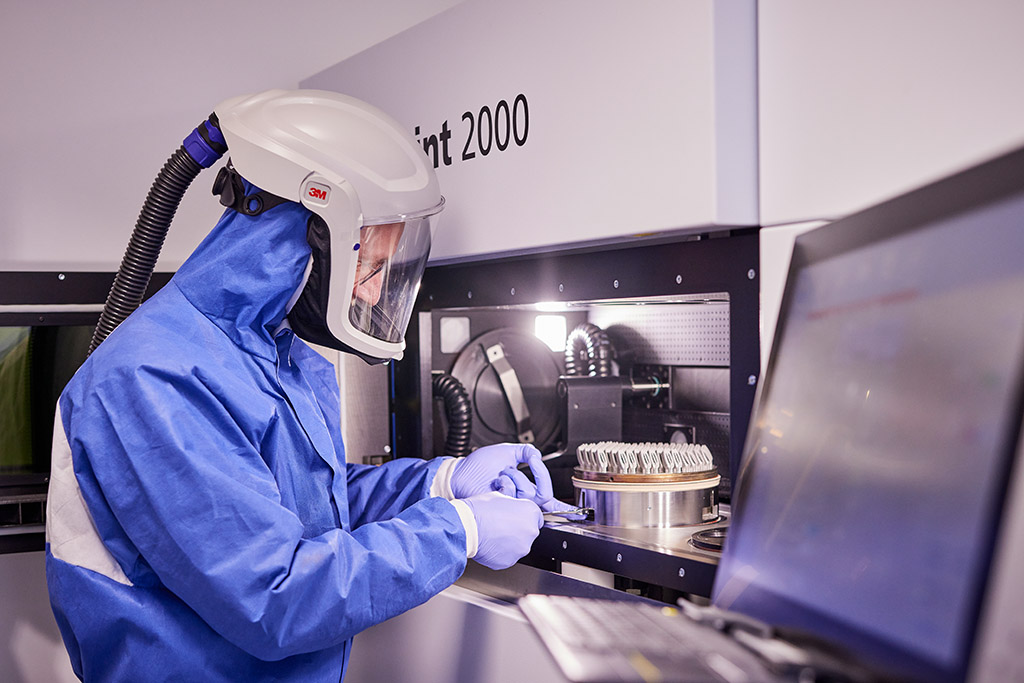



The common term for additive manufacturing is 3-D printing. In precision language, this is the PBF/LBM process. This innovative production process opens up completely new possibilities for our industry. We have been relying on this forward-looking technology since 2015; numerous successful projects have confirmed this focus with top-quality results.
- Complete modules can be manufactured in their entirety, thereby eliminating the need for assembly.
- The number of individual parts per module is reduced – and thus the post-processing and assembly time.
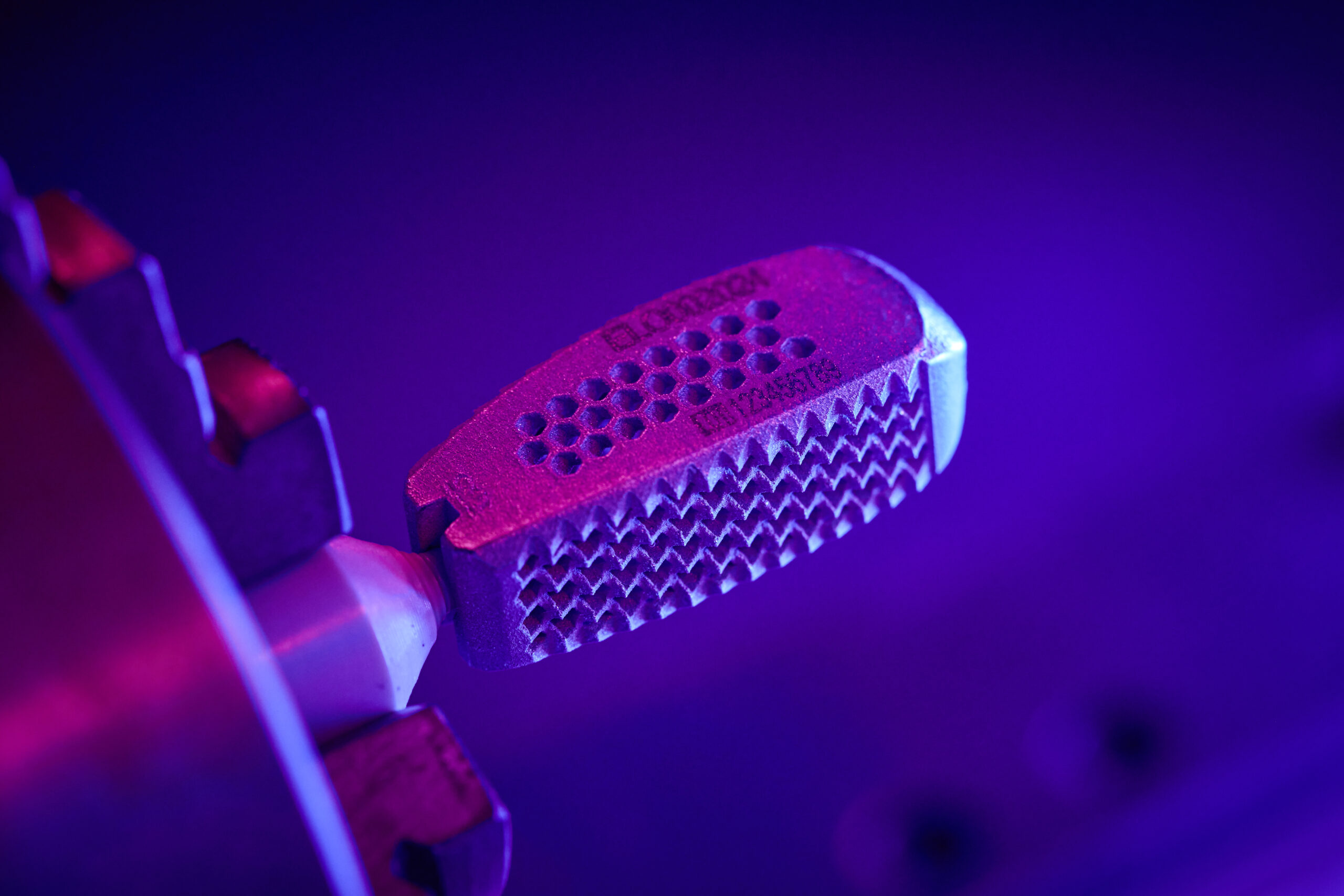
- Many medical technology designs benefit from the freedom of geometry. For example in porous spinal cages, which achieve better bone attachment thanks to macrostructured surfaces.
- Topology-optimized geometries are produced 1:1 with the 3-D printer. The component rigidity (e.g., of implants) can be set as a parameter.
- New ideas or changes can be created on the machine without a great deal of set-up work, thereby enabling rapid prototype grinding.
- The method is cost-effective, especially when complex structures are to be produced.
Weight
Material consumption
Assembly effort
Component merging/reduction
Costs
Range of functions
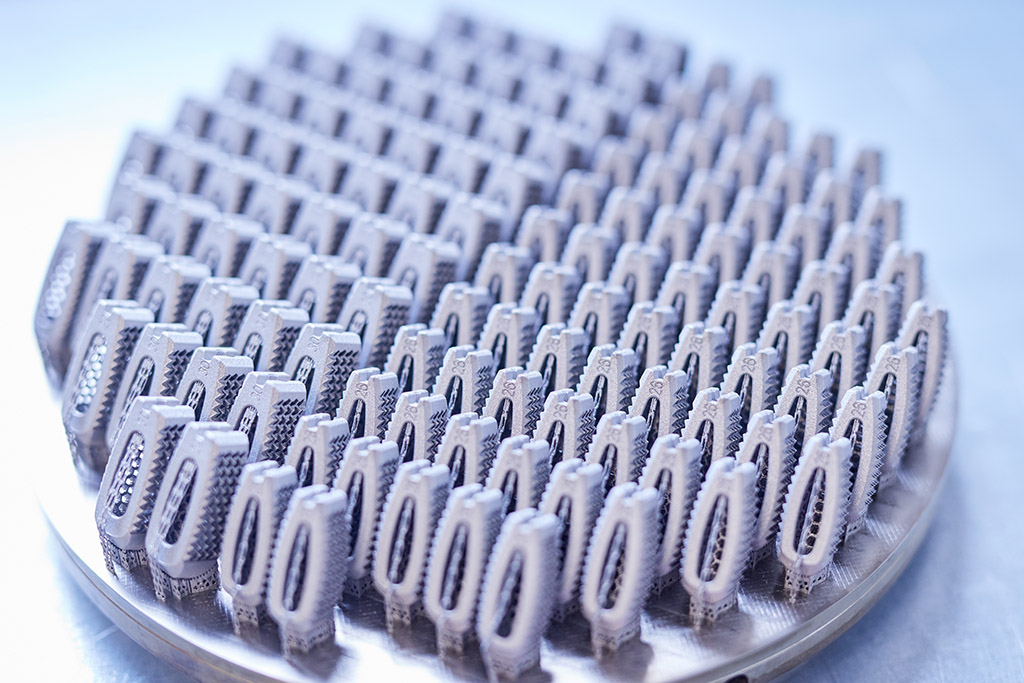
Are you looking for large components or high volumes? We can handle these. The core of our innovative technology park for shapeless production is our high-performance printer with fiber lasers. This enables us to implement cylindrical projects with a diameter of up to 200 mm and a height of 200 mm. This means that also large components can be realized. Depending on the component size, high project quantities can be achieved.
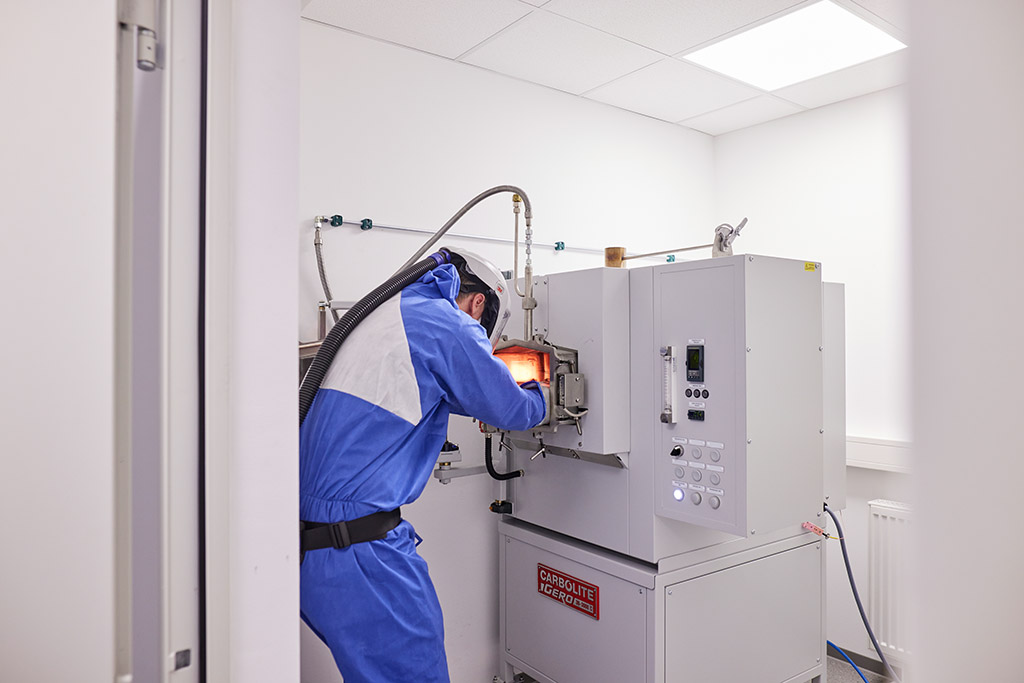

The multi-lasers work simultaneously – another plus for economical production and considerable time saving. In CPM Precision production, the laser printer applies layers that are only 20 μm thick. These fine layers offer a particularly high level of detail. For example, in the surface finish. The subsequent heat treatment is carried out in a chamber furnace under a protective gas atmosphere. The powder is prepared and handled under inert gas.
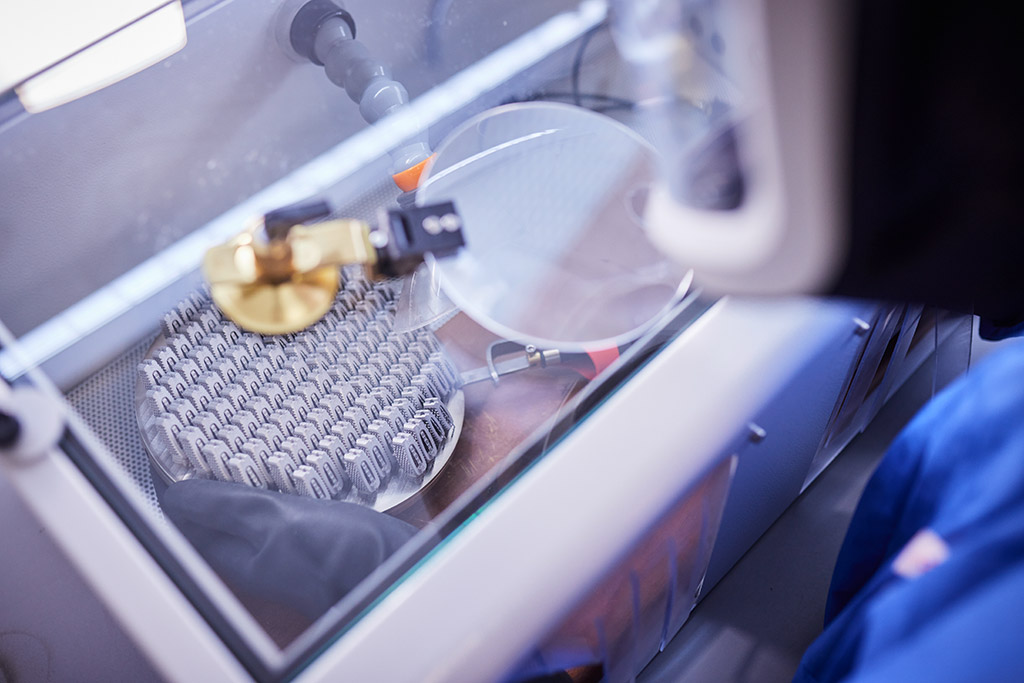

If further processing is required, we rely on mechanical solutions using the latest machine generations such as CNC fixed and sliding headstock lathes, and CNC milling machines.
The powder is handled in the complete absence of ambient oxygen. Intelligent software solutions carefully monitor the entire construction process. The process is checked after each individual layer is applied by the multi-laser. In this validated process, we use powder bed monitoring and other methods. Sensors record all relevant data. Their evaluation enables us to recognize potential errors at an early stage and react quickly. This allows us to keep a constant watch on the entire production and meet our high standards in terms of safety, efficiency, and quality.


Benefit from our extensive experience and discover the advantages of the additive manufacturing process. Get in touch with us. We will be happy to advise you.
What is Additive Manufacturing?
Additive manufacturing (AM) is the umbrella term for manufacturing processes that build up work pieces layer by layer instead of removing material from a block of material by machining (as is the case with other processes) and thus carving out the component. The process is used in almost all industrial sectors that manufacture metal, ceramic, and plastic components. The manufacturing process is particularly well suited to the complex requirements of medical technology and offers numerous advantages.
Additive vs. Conventional Manufacturing – Which Method Is Better?
Thanks to our modern machinery, we offer both machining and additive manufacturing. This gives us a broad methodological base and prepares us for complex production. Each method has its advantages. In this way, additive manufacturing can save material, time, and energy and cover a wide range of functions. On the other hand, machining manufacturing continues to score high in terms of precision and flexible application options. Our highly qualified specialists with many years of expertise in both production areas will be happy to help you with your individual selection. It is also possible to combine both methods.
Which Additive Processes Does CPM Precision Use?
The umbrella term “additive manufacturing processes” covers several similar production methods. The distinction is made according to methodological details in production:
- Powder bed processes such as laser melting or PBF/LBM: A powdery material is selectively melted layer by layer using a laser.
- Liquid material processes (e.g., stereolithography): Here, the laser hardens resin mixed with the desired material.
- Free-space processes – for example, the fused deposition modeling (FDM) process: A printer with a heatable nozzle moves freely in space (hence the name) and deposits the finest strands of the material, which then harden.
We use the laser-based powder bed fusion of metals (PBF-LB/M) to manufacture high-quality medical technology products. This process is ideal for producing components that have to meet specific surface conditions yet guarantee a high dynamic and thermal load capacity. With PBF-LB/M, it is possible to produce complex geometries with thin-walled surfaces through the direct fusion of the starting material.
Which Materials Does CPM Precision Use in Additive Manufacturing?
Our medical products from additive manufacturing are made exclusively from titanium. This guarantees maximum purity. We use titanium grades 4 and 23. The latter corresponds to Grade 5 but is especially suitable for more stringent requirements such as those found in medical technology. The alloy features good biocompatibility and excellent properties. Compared with Grade 5 titanium, Grade 23 has a particularly high purity. The interstitial elements are reduced, thereby improving both the fracture toughness and the ductility of the material. The alloy also has a low intrinsic weight. It is therefore ideal for surgical implants or orthodontic appliances.
By the way: The qualification of our printing parameters for titanium grade 4 is not the general standard and is by no means common in the industry. In cooperation with our machine manufacturer Trumpf, we were the first user to qualify the laser parameters for pure titanium grade 4, thereby expanding our manufacturing expertise to the highest level.